Understanding Centrally Mediated Abdominal Pain Syndrome (CAPS)
Centrally Mediated Abdominal Pain Syndrome (CAPS) is a complex condition that affects many individuals suffering from gastrointestinal (GI) disorders. Easily confused with more common conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), CAPS is characterized by chronic and severe abdominal pain that is not linked to dietary habits or bowel patterns. Unlike other GI disorders, CAPS lacks identifiable abnormalities on diagnostic tests, making it particularly challenging for both patients and healthcare providers.
The Science Behind the Pain
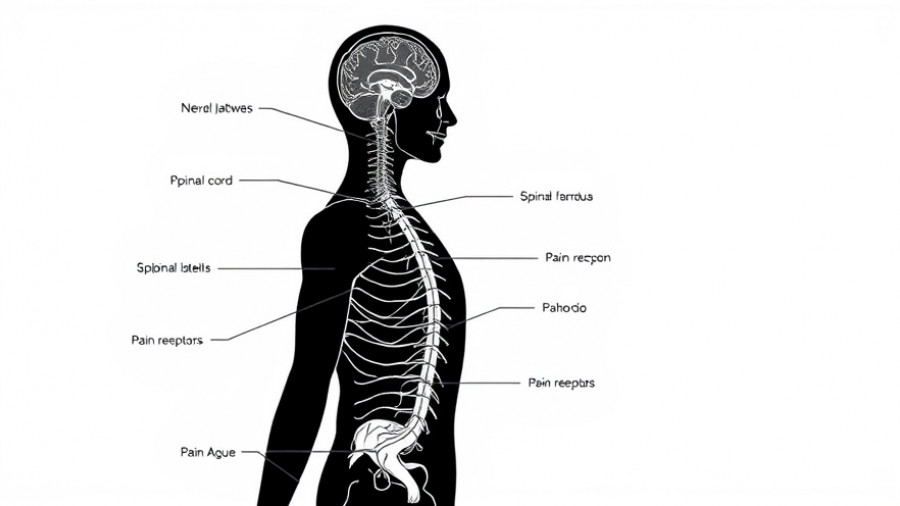
To grasp the intricacies of CAPS, it's essential to understand the pathophysiology behind it. Nerve impulses connected to the abdominal region travel to the spinal cord and various cerebral areas, influencing how pain is felt. Interestingly, emotions and past experiences significantly impact pain perception. Stressful events, like loss or trauma, can trigger or exacerbate symptoms, creating a vicious cycle where fear of pain leads to heightened sensitivity. This increase in sensitivity can transform typical gut sensations into agonizing experiences, driven by a phenomenon known as visceral hypersensitivity.
The Importance of Psychological Well-being
Psychological factors play a substantial role in the management of CAPS. Stress management, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and relaxation techniques are critical in addressing the patient’s experience. Patients report that learning to divert attention away from pain can reduce its intensity, akin to how athletes can sometimes ignore pain during a game. Patient support, including family and peer networks, enhances their resilience in coping with CAPS.
Multi-Faceted Treatment Strategies for CAPS
Treatment for CAPS often requires a thoughtful, multi-faceted approach. This involves a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies aimed at reducing pain perception and enhancing the overall quality of life. Recent guidelines emphasize using low-dose tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) to manage pain effectively. It's essential to know that these medications can take weeks to show results, and patience with the treatment process is necessary.
Collaboration is Key: The Patient-Doctor Partnership
One vital aspect of treating CAPS is the collaborative partnership between the patient and the doctor. Effective communication about symptoms, treatment goals, and feedback on what works or does not work form the backbone of successful treatment strategies. When patients feel heard and understood, their treatment and management experience significantly improves, leading to better outcomes.
Conclusion: Empowering Yourself Against CAPS
Centrally Mediated Abdominal Pain Syndrome remains a challenging yet manageable condition. By understanding the intertwining of physical pain and emotional well-being, patients can adopt a proactive approach to their treatment. Combining medical therapies with psychological and lifestyle strategies can pave the way for improved quality of life. Remember, you're not alone; support from professionals and loved ones can make a world of difference.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment